Learning Center
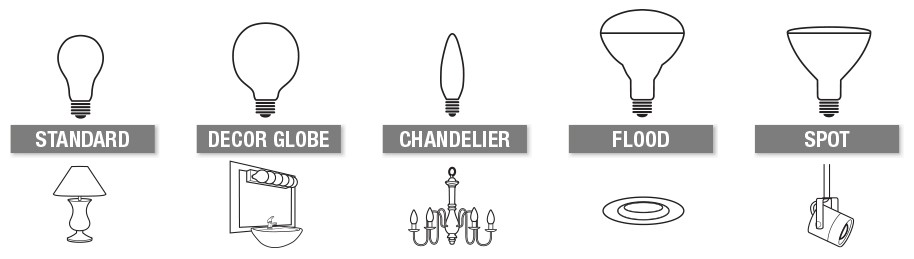
Light Bulbs
Batteries
Non-rechargeable (Primary) Batteries
Types of non-rechargeable (primary) batteries 
- Super Heavy Duty Batteries also known as Carbon Zinc batteries are the inexpensive alternative to Alkaline batteries. They have a shorter shelf life compared to Alkaline batteries but they are also less expensive. They are ideal for a wide range of low to medium drain devices such as flashlights, portable radios, recorders, remote controls and clocks.
- Alkaline Batteries are the most widely used batteries in North America due to their long-lasting performance and long shelf life combined with good value. Alkaline batteries are used for general purpose applications including lighting, photographic equipment, toys, communication equipment, radio and television applications, tape recorders and instruments and other medium to high drain devices. It is recommended to opt for Alkaline Ultra Batteries for higher drain devices such as digital cameras, MP3 players, video game controls and high-powered toys.
- Lithium Batteries offer high performance due to their light weight, high voltage and wider operating temperature range. Because of their outstanding performance and characteristics, lithium batteries are used in a variety of applications including cameras, memory backup circuits, calculators, watches, security devices, etc. However lithium batteries still remain a small percentage of the primary battery market due to their high cost.
| Low Drain (Super Heavy Duty) |
Moderate Drain (Super Heavy Duty/Alkaline) |
High Drain (Alkaline/Alkaline Ultra) |
|
| AA | Remote control, radio, clock | Toy, lighting, tape player | Games, CD’s, photoflash, digital camera |
| AAA | Radio, remote control | Lighting | Games, digital audio, digital camera, photoflash |
| C | Radio | Lighting, toy | Portable stereo |
| D | Radio | Lighting, toy | Portable stereo |
| 9V | Smoke detector, clock, radio | Garage opener, baby monitor | Toy |
Button Cells are non-rechargeable, dry-cell batteries commonly in Alkaline (AG) or Silver Oxide (SG) chemistries. Silver Oxide chemistry batteries have more capacity than Alkaline button cells and therefore more costly. Button batteries are commonly used in low-drain devices such as wrist watches, pocket calculators, medical devices such as blood pressure monitors and other small electronic devices. Zinc air technology is used for button cells for hearing aid devices. Lithium cells (CR) are somewhat larger and have a higher voltage than button cells and referred to as coin cells.
| Commercial Name | Applications |
| AG1,SG1 | Watches, Toys, Health care, Calculators |
| AG4, SG4 | Watches, Calculators |
| AG10, SG10 | Watches, Toys, Fitness, Calculators |
| AG13, SG13 | Watches, Electronics,Toys, Health Care, Automotive |
| CR2016 | Watches, Electronics,Toys, Game & Books, Fitness, Health Care, Automotive |
| CR2025 | Watches, Electronics,Toys, Game & Books, Automotive |
| CR2032 | Watches, Electronics,Toys, Game & Books, Fitness, Health Care, Automotive |
| Commercial Name | Dimension (Diameter x Height) |
IEC name | Equivalent |
| AG1 SG1 |
0.268" x 0.083" 6.8 x2.1 mm |
LR60 | 363, 364, SR60, L621, LR620, LR621, SR621, V364, V531 |
| AG4 SG4 |
0.268" x 0.103" 6.8 x2.6 mm |
LR66 | 376, 377, L626, LR626, SR66, SR626, SR626SW |
| AG10 SG10 |
0.457" x 0.12" 11.6 x3.1 mm |
LR54 | 389, 390, 189, LR113, L1131, LR1130, SR54, LR1131, SR1130, SR1130SW |
| AG13 SG13 |
0.457" x 0.213" 11.6 x5.4 mm |
LR44 | 303, 357, A76, L154, L1154, LR1154, SR44 |
| Commercial Name | Dimension (Diameter x Height) |
IEC/ANSI name | Other common names |
| 10 |
0.228" x 0.142" 5.8 x 3.6 mm |
PR70/7005ZD | Yellow tab |
| 13 | 0.311" x 0.213" 7.9 x 5.4 mm |
PR48/7000ZD | Orange tab |
| 312 | 0.311" x 0.142" 7.9 x 3.6 mm |
PR41/7002ZD | Brown tab |
| 675 | 0.457" x 0.213" 11.6 x 5.4 mm |
PR44/7003ZD | Blue tab |
-
Discard button batteries carefully.
-
Do not allow children to play with button batteries, and keep button batteries out of your child's reach.
-
Caution hearing aid users to keep hearing aids and batteries out of the reach of children.
-
Never put button batteries in your mouth for any reason as they are easily swallowed accidentally.
-
Always check medications before ingesting them. Adults have swallowed button batteries mistaken for pills or tablets.
-
Keep remotes and other electronics out of your child's reach if the battery compartments do not have a screw to secure them. Use tape to help secure the battery compartment.
-
If a button battery is ingested, immediately seek medical attention. The National Battery Ingestion Hotline is available anytime at (202) 625-3333 (call collect if necessary), or call your poison center at (800) 222-1222.
Rechargeable (Secondary) Batteries
Secondary or rechargeable batteries are now widely used in various applications. Small secondary batteries are used increasingly to power portable devices such as tools, toys, lighting, digital cameras, radio and more significantly in consumer electronic devices. The energy capacity of a battery is measured in milli Ampere hour (mAh). The higher the energy capacity of a battery, the more electrical energy it can store. The most common types of rechargeable batteries used for power portable devices are Nickel-cadmium (NiCd) and Nickel-metal hydride (NiMH).
-
Nickel-cadmium batteries have a good low-temperature and high-rate performance capability but a lower discharge rate compared to NiMH. They are often used in low drain devices such as clocks, remote controls and solar lights. Due to the environmental concern with the use of cadmium, popularity of NiCd batteries has been decreasing in the past years. They also have lower capacity than other competitive batteries.
-
Nickel-metal hydride batteries provide a great alternative to primary batteries. NiMH batteries have low discharge capability and can hold up to 80% of their charge for 1 year if stored in room temperature. They also hold up to 3 times more than the capacity of Nickel Cadmium rechargeable batteries. A NiMH battery can be charged and discharged hundreds of times and this makes it a highly sustainable option as opposed to primary batteries. To get the most out of your NiMH batteries, it is recommended to recharge them to their full capacity, limit the extent of overcharge and avoid high temperatures and temperature fluctuations.
-
Alkaline batteries and carbon zinc batteries can be safely disposed of with normal household waste. It is important not to dispose of large amounts of batteries in a group. Some communities offer recycling or collection of batteries. Consumers should contact their local municipality for this info.
-
Rechargeables, lithium, alkaline & silver oxide with mercury content & zinc air should be recycled.
-
To find out where to recycle rechargeables, go to www.call2recycle.org. For Canada, go to www.call2recycle.ca.
Below guidelines should be followed to assure that batteries and devices operate reliably:
-
Store batteries in a dry place at room temperature. Batteries are sensitive to high and low temperatures.
-
Keep contacts clean, both on the battery and in the device.
-
Remove batteries from devices that will not be used for long periods of time (months or longer).
-
Choose the battery for the intended application. Follow the recommendations supplied with the device.
-
Never charge the battery unless the battery label specifically states the battery is rechargeable.